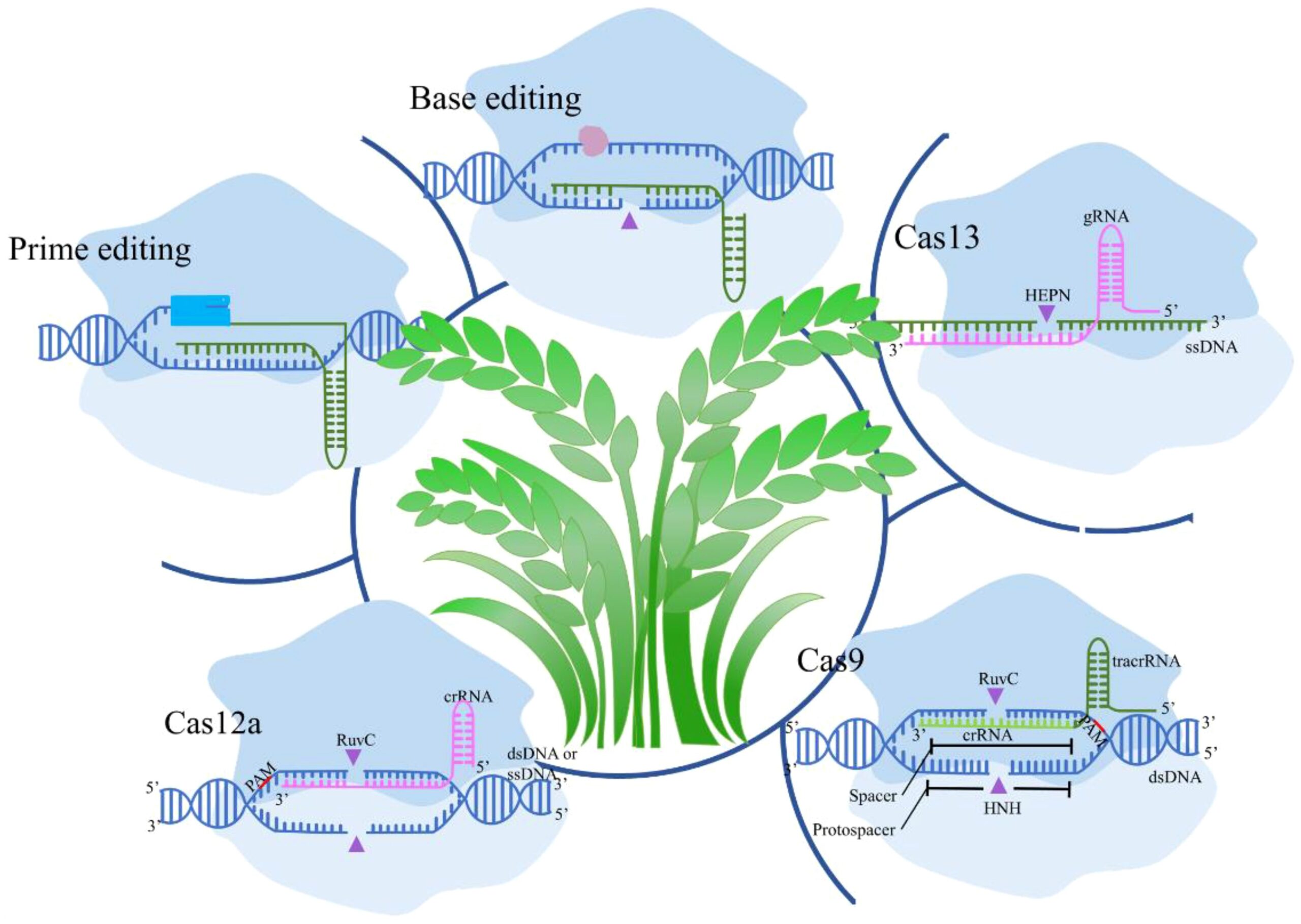
CRISPR gene-editing technology is rapidly transforming modern agriculture, enabling scientists and farmers to develop crops that are more productive, resilient, and sustainable. By precisely modifying plant genetics, CRISPR allows for targeted improvements in yield, disease resistance, and climate adaptability, offering promising solutions to some of the biggest challenges facing global food production.
Unlike traditional breeding methods, which can take years or even decades, CRISPR enables rapid and precise genetic modifications. Researchers can identify specific genes responsible for traits such as drought tolerance, pest resistance, or improved nutrient content and modify them without introducing foreign DNA. This precision not only accelerates the development of superior crop varieties but also minimizes unintended effects, making the technology safer and more predictable.
Recent studies have demonstrated the potential of CRISPR-edited crops to withstand environmental stresses. For example, scientists have developed wheat and rice varieties with enhanced resistance to fungal diseases, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Similarly, crops such as maize and soybeans are being engineered to tolerate extreme temperatures and water scarcity, addressing challenges posed by climate change. These innovations have the potential to stabilize yields, safeguard food security, and reduce the environmental footprint of agriculture.
Beyond improving resilience, CRISPR is also contributing to enhanced nutritional quality. Researchers are using the technology to increase the levels of essential vitamins, minerals, and proteins in staple crops, providing a pathway to combat malnutrition in vulnerable populations. Additionally, the efficiency of CRISPR can support sustainable farming practices by decreasing the reliance on fertilizers, pesticides, and water, ultimately promoting environmental sustainability.
While the promise of CRISPR in agriculture is significant, regulatory frameworks and public acceptance remain key considerations. Governments, research institutions, and industry stakeholders are working to establish guidelines for safe and responsible use, ensuring that the technology benefits both farmers and consumers. Transparent communication about its applications and advantages is also critical for building public trust.
The integration of CRISPR technology into agriculture represents a major step toward the future of farming. By enhancing crop productivity, disease resistance, and climate resilience, CRISPR has the potential to reshape global agriculture, ensuring that food systems remain robust in the face of population growth, environmental pressures, and changing consumer demands.














